“Truly Astonishing” – Discovery of 500-Million-Year-Old “Pompeii” Trilobite Fossils Shake Up Scientific Understanding of the Long-Extinct Group


Artistic reconstruction of two species of trilobite an instant before burial in a flow of volcanic ash 510 million years ago. Credit: Prof. A. El Albani, Univ. Poitiers
Researchers have discovered exceptionally preserved “Pompeii” trilobite fossils in Morocco, providing new insights into the anatomy and preservation of these ancient creatures through advanced imaging techniques.
Researchers have described some of the best-preserved three-dimensional trilobite fossils ever discovered. These over 500-million-year-old fossils were collected in the High Atlas of Morocco and are being referred to as “Pompeii” trilobites by scientists due to their remarkable preservation in ash.
The trilobites, from the Cambrian period, have been the subject of research by an international team of scientists, led by Prof Abderrazak El Albani, a geologist based at the University of Poitiers and originally from Morocco. The team included Dr Greg Edgecombe, a paleontologist at the Natural History Museum.
Dr Greg Edgecombe comments: “I’ve been studying trilobites for nearly 40 years, but I never felt like I was looking at live animals as much as I have with these ones. I’ve seen a lot of soft anatomy of trilobites, but it’s the 3D preservation here that is truly astounding. An unexpected outcome of our work is discovering that volcanic ash in shallow marine settings could be a bonanza for exceptional fossil preservation.”
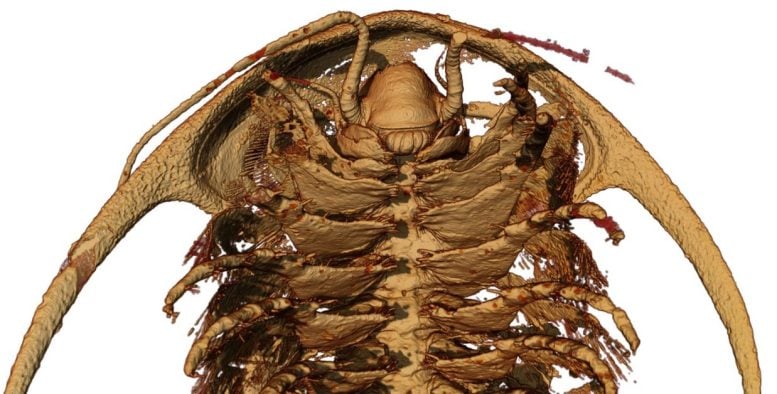
Microtomographic reconstruction of the head and anterior trunk (“body”) limbs of the trilobite Protolenus (Hupeolenus) in ventral view. Credit: Arnaud Mazurier, IC2MP, Univ. Poitiers
Due to their hard, calcified exoskeleton often being well-preserved in the fossil record, trilobites are some of the best-studied fossil marine animals. Over 20,000 species have been described by paleontologists over the past two centuries.
However, until now, comprehensive scientific understanding of this phenomenally diverse group has been limited by the relative scarcity of soft tissue preservation. Owing to the fact the Moroccan trilobites were encased in hot ash in seawater, their bodies fossilized very quickly as the ash transformed to rock – meeting a similar end to the inhabitants of Pompeii following the eruption of Mount Vesuvius.
The ash molds preserved each segment of their bodies, their legs, and even the hair-like structures that ran along the appendages. The trilobites’ digestive tract was also preserved after it filled with ash. Even small “lamp shells” attached to the trilobites’ exoskeleton remained attached by fleshy stalks as they were in life.
Supplementary video. Credit: Greg Edgecombe
New Discoveries and Methods
Lead author, Prof Abderrazak El Albani, comments: “As a scientist who has worked on fossils from different ages and locations, discovering fossils in such a remarkable state of preservation within a volcanic setting was a profoundly exhilarating experience for me. I think pyroclastic deposits should become new targets for study, given their exceptional potential for trapping and preserving biological remains, including delicate soft tissues. These findings are anticipated to lead to significant discoveries about the evolution of life on our planet Earth.”
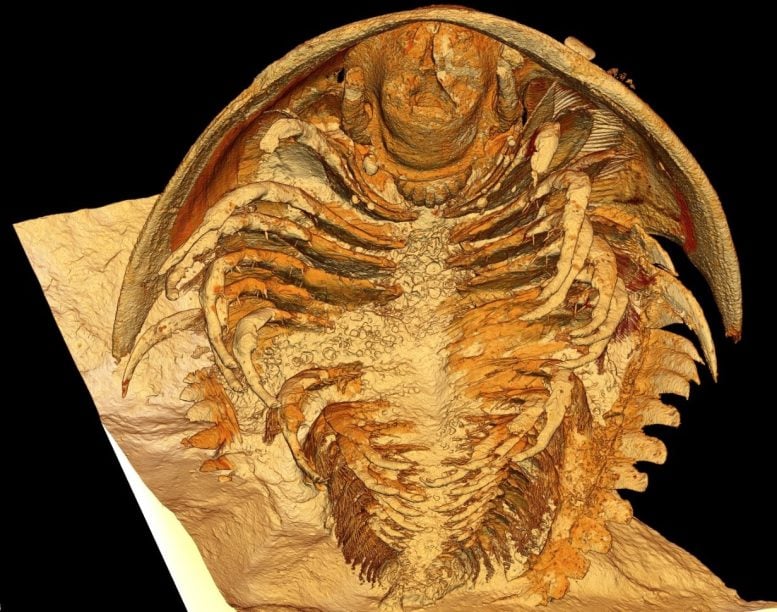
Microtomographic reconstruction of the trilobite Gigoutella mauretanica in ventral view. Credit: Arnaud Mazurier, IC2MP, Univ. Poitiers
Using CT scanning and computer modeling of virtual X-ray slices, the researchers discovered that appendages found at the edge of the mouth had curved spoon-like bases but were so small they had gone undetected in less perfectly preserved fossils. In fact, it had previously been thought that trilobites had three pairs of head appendages behind their long antennae but both Moroccan species in this study showed that there were four pairs.
A fleshy lobe covering the mouth, called a labrum, was documented for the first time in trilobites.
Co-author Harry Berks, from the University of Bristol, added: “The results revealed in exquisite detail a clustering of specialized leg pairs around the mouth, giving us a clearer picture of how trilobites fed. The head and body appendages were found to have an inward-facing battery of dense spines, like those of today’s horseshoe crabs.”
Reference: “Rapid volcanic ash entombment reveals the 3D anatomy of Cambrian trilobites” by Abderrazak El Albani, Arnaud Mazurier, Gregory D. Edgecombe, Abdelfattah Azizi, Asmaa El Bakhouch, Harry O. Berks, El Hafid Bouougri, Ibtissam Chraiki, Philip C. J. Donoghue, Claude Fontaine, Robert R. Gaines, Mohamed Ghnahalla, Alain Meunier, Alain Trentesaux and John R. Paterson, 27 June 2024, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.adl4540



