Scientists Use Biomechanics To Decode the Secrets of Bad Hair Days


Researchers at Trinity College Dublin, led by Professor David Taylor, have developed a machine, the “Moving Loop Fatigue machine,” to study hair-splitting, traditionally a little-understood phenomenon. They successfully reproduced hair splits, shedding light on the biomechanics of hair damage and paving the way for future studies on the impact of cosmetic treatments on hair quality.
Researchers have developed a machine to study hair splitting, revealing new insights into how mechanical stress and treatments like bleaching impact hair. This research provides a foundation for future studies aimed at improving hair care and cosmetics.
Academics are often accused of “splitting hairs,” but a team at Trinity College Dublin has now devised a machine to do just that. We all have a bad hair day from time to time, and split ends are a common problem. However, the science behind this kind of hair damage is poorly understood, which is why the Trinity team, led by Professor David Taylor, is investigating this knotty problem.
Prof. Taylor’s research in the Trinity Centre for Biomedical Engineering covers all kinds of natural materials, from human bone to seashells but he had never worked on hair. So, when leading cosmetics company L’Oreal approached him, he was happy to accept the challenge.
Working with colleagues, he developed the “Moving Loop Fatigue machine”, which has been expertly designed to recreate what happens when tangled hair is combed out. The results have just been published in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface Focus.
Experimental Findings
Two types of hair were tested: some from a person who suffered from split ends and some from a person who didn’t. Using the machine, the team was able to generate splits in both types of hair, but the splitting-prone hair split more quickly and generated splits that were much longer. Additionally, when bleached, the hair from the person who didn’t suffer from split ends started to split similarly to the splitting-prone sample.
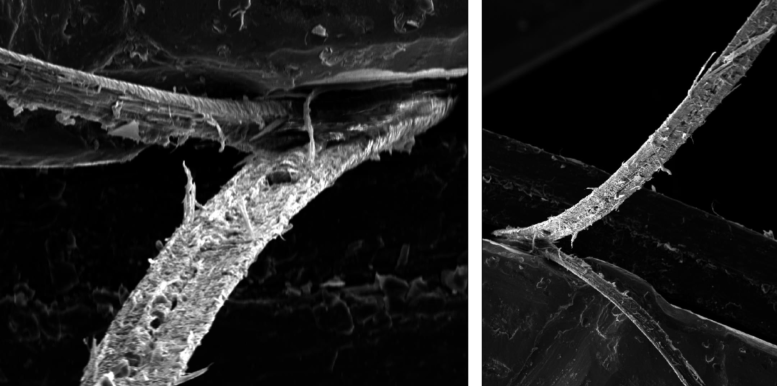
An electron microscope image of a hair, split along its length. Credit: Prof. David Taylor, Trinity College Dublin
Isobel Duffy, one of the researchers on the team, added: “We were amazed at how well the machine worked – often, a single strand of hair split into two along its whole length, in the same way, that hair does when some people dry and comb it before starting their days. Now we can create splits in a reproducible way we can go on to study why some people’s hair splits and some don’t, and better investigate the effects that some cosmetic treatments have on hair quality.”
Future Research Directions
Prof. David Taylor said: “This work constitutes a first step in developing a scientific approach to better understanding the biomechanics of hair-splitting. It paves the way for future studies, including a more comprehensive experimental program involving a larger number of donors with different hair types – including curly hair – and more detailed studies that could incorporate the effects of humidity, temperature, and different treatments.
“Hair is a complex material and it is surprising how little we know about it. In time our work may change that, with implications for the cosmetics industry and the millions of people across the globe that want to take first-rate care of their hair.”
Another team member, Robert Teeling, added: “When I started as an Engineering student in Trinity I didn’t think I would spend my Masters’ year testing hair. But it turned out to be a great project: I designed and built a new type of machine from scratch and made a real contribution to science. I learned that hair is a material like any other: it can break through mechanical forces, in this case when you comb or brush it, and it’s sensitive to how you treat it.”
Reference: “The biomechanics of splitting hairs” by David Taylor, Ellen Barton, Isobel Duffy, Ramona Enea-Casse, Guillaume Marty, Robert Teeling and Roberto Santoprete, 1 June 2024, Interface Focus.
DOI: 10.1098/rsfs.2023.0063



