Scientists Have Uncovered Autism’s Earliest Biological Signs

Researchers at UC San Diego have discovered that differences in autism severity are linked to brain development in the embryo, with larger brain organoids correlating with more severe autism symptoms. This insight into the biological basis of autism could lead to targeted therapies.
An unusually large brain may be the first sign of autism — and visible as early as the first trimester, according to a recent study conducted by UCSD.
Some children with profound autism face lifelong challenges with social, language, and cognitive skills, including the inability to speak. In contrast, others exhibit milder symptoms that may improve over time.
The disparity in outcomes has been a mystery to scientists, until now. A new study, published in Molecular Autism by researchers at the University of California San Diego, is the first to shed light on the matter. Among its findings: The biological basis for these two subtypes of autism spectrum disorder develops in the first weeks and months of embryonic development.
Researchers used inducible pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from blood samples of 10 toddlers with autism and six neurotypical “controls” of the same age. Able to be reprogrammed into any kind of human cell, they used the iPSCs to create brain cortical organoids (BCOs) — models of the brain’s cortex during the first weeks of embryonic development. The veritable “mini-brains” grown from the stem cells of toddlers with autism grew far larger — roughly 40% — than those of neurotypical controls, demonstrating the growth that apparently occurred during each child’s embryonic development.
Link Between Brain Overgrowth and Autism Severity
“We found the larger the embryonic BCO size, the more severe the child’s later autism social symptoms,” said UC San Diego’s Eric Courchesne, the study’s lead researcher and Co-Director of the Autism Center of Excellence in the neuroscience department. “Toddlers who had profound autism, which is the most severe type of autism, had the largest BCO overgrowth during embryonic development. Those with mild autism social symptoms had only mild overgrowth.”
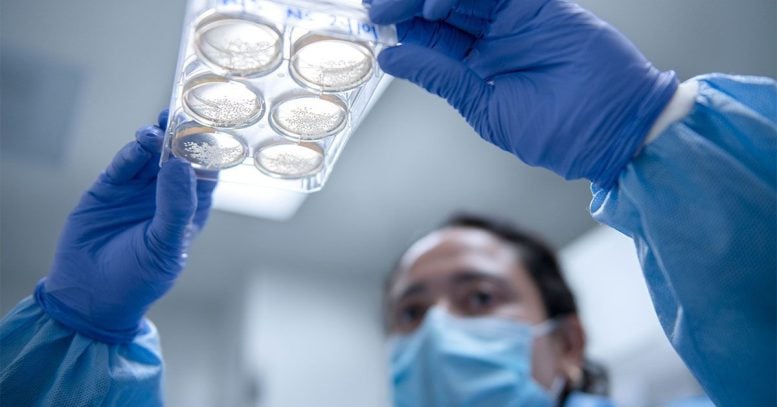

Brain cortical organoids (BCOs) created by Dr. Alysson Muotri shown in a 2019 file photo. Researchers at the University of California San Diego used stem cells from toddlers with autism and created BCOs from them. The stem cells of toddlers with autism developed into larger BCOs, they discovered. Toddlers with autism also had larger brain volumes, according to MRI. Credit: UC San Diego Health Sciences
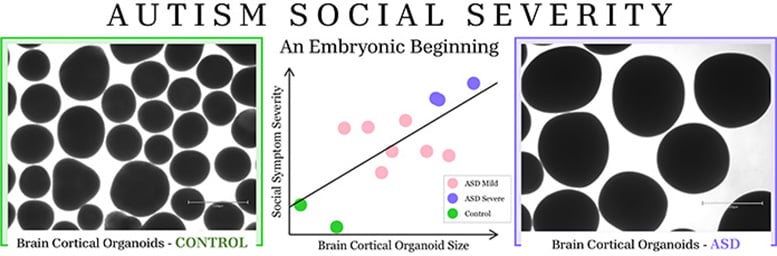
Using brain cortical organoids (BOCs) and comprehensive social brain imaging, social eye tracking and social behavior testing, Courchesne and colleagues discovered that profound autism begins during embryogenesis. The greater the overgrowth of embryonic BCOs, the more severe the autism social symptoms at toddler ages. Toddlers who have profound autism, which is the most severe type of autism, have the most extreme BCO overgrowth during embryonic development. Credit: UC San Diego Health Sciences
In remarkable parallel, the more overgrowth a BCO demonstrated, the more overgrowth was found in social regions of the profound autism child’s brain and the lower the child’s attention to social stimuli. These differences were clear when compared against the norms of hundreds and thousands of toddlers studied by the UC San Diego Autism Center of Excellence. What’s more, BCOs from toddlers with profound autism grew too fast as well as too big.
“The bigger the brain, the better isn’t necessarily true,” agreed Alysson Muotri, Ph.D., director of the Sanford Stem Cell Institute’s Integrated Space Stem Cell Orbital Research Center at the university. Muotri and Courchesne collaborated on the study, with Muotri contributing his proprietary BCO-development protocol that he recently shared via publication in Nature Protocols, as well as his expertise in BCO measurement.
Implications for Therapy and Further Research
Because the most important symptoms of profound autism and mild autism are experienced in the social affective and communication domains, but to different degrees of severity, “the differences in the embryonic origins of these two subtypes of autism urgently need to be understood,” Courchesne said. “That understanding can only come from studies like ours, which reveals the underlying neurobiological causes of their social challenges and when they begin.”

Brain cortical organoids (BCOs) created by Dr. Alysson Muotri shown in a 2019 file photo. Researchers at the University of California San Diego used stem cells from toddlers with autism and created BCOs from them. The stem cells of toddlers with autism developed into larger BCOs, they discovered. Toddlers with autism also had larger brain volumes, according to MRI. Credit: UC San Diego Health Sciences
One potential cause of BCO overgrowth was identified by study collaborator Mirian A.F. Hayashi, Ph.D., professor of pharmacology at the Federal University of São Paulo in Brazil, and her Ph.D. student João Nani. They discovered that the protein/enzyme NDEL1, which regulates the growth of the embryonic brain, was reduced in the BCOs of those with autism. The lower the expression, the more enlarged the BCOs grew.
“Determining that NDEL1 was not functioning properly was a key discovery,” Muotri said.
Courchesne, Muotri, and Hayashi now hope to pinpoint additional molecular causes of brain overgrowth in autism — discoveries that could lead to the development of therapies that ease social and intellectual functioning for those with the condition.
References: “Embryonic origin of two ASD subtypes of social symptom severity: the larger the brain cortical organoid size, the more severe the social symptoms” by Eric Courchesne, Vani Taluja, Sanaz Nazari, Caitlin M. Aamodt, Karen Pierce, Kuaikuai Duan, Sunny Stophaeros, Linda Lopez, Cynthia Carter Barnes, Jaden Troxel, Kathleen Campbell, Tianyun Wang, Kendra Hoekzema, Evan E. Eichler, Joao V. Nani, Wirla Pontes, Sandra Sanchez Sanchez, Michael V. Lombardo, Janaina S. de Souza, Mirian A. F. Hayashi and Alysson R. Muotri, 25 May 2024, Molecular Autism.
DOI: 10.1186/s13229-024-00602-8
“Generation of ‘semi-guided’ cortical organoids with complex neural oscillations” by Michael Q. Fitzgerald, Tiffany Chu, Francesca Puppo, Rebeca Blanch, Miguel Chillón, Shankar Subramaniam and Alysson R. Muotri, 3 May 2024, Nature Protocols.
DOI: 10.1038/s41596-024-00994-0
Co-authors of the study include Vani Taluja, Sanaz Nazari, Caitlin M. Aamodt, Karen Pierce, Kuaikuai Duan, Sunny Stophaeros, Linda Lopez, Cynthia Carter Barnes, Jaden Troxel, Kathleen Campbell, Tianyun Wang, Kendra Hoekzema, Evan E. Eichler, Wirla Pontes, Sandra Sanchez Sanchez, Michael V. Lombardo and Janaina S. de Souza.
This work was supported by grants from the National Institute of Deafness and Communication Disorders, the National Institutes of Health, the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine and the Hartwell Foundation. We thank the parents of the toddlers in San Diego whose stem cells were reprogrammed to BCOs.
Disclosures: Muotri is a co-founder and has equity interest in TISMOO, a company dedicated to genetic analysis and human brain organogenesis, focusing on therapeutic applications customized for autism spectrum disorders and other neurological disorders origin genetics. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of California San Diego in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies. Eichler is a scientific advisory board member of Variant Bio, Inc. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.



