Are We Really Made of Stardust?

Researchers are exploring how cosmic radiation interacting with ice particles can form prebiotic molecules, with significant implications for understanding the origins of life in the universe and potential applications in medical and environmental fields.
Cosmic Origins and Prebiotic Chemistry
Who are we? Why are we here? As the Crosby, Stills, Nash & Young song suggests, we are stardust, the result of chemistry occurring throughout vast clouds of interstellar gas and dust. To better understand how that chemistry could create prebiotic molecules — the seeds of life on Earth and possibly elsewhere — researchers investigated the role of low-energy electrons created as cosmic radiation traverses through ice particles. Their findings may also inform medical and environmental applications on our home planet.
Undergraduate student Kennedy Barnes will present the team’s results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2024 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in person Aug. 18-22; it features about 10,000 presentations on a range of science topics.
Historical Insights and Research Aims
“The first detection of molecules in space was made by Wellesley College alum Annie Jump Cannon more than a hundred years ago,” says Barnes, who, with fellow undergraduate Rong Wu, led this study at Wellesley, mentored by chemistry professor Christopher Arumainayagam and physics professor James Battat. Since Cannon’s discovery, scientists have been interested in finding out how extraterrestrial molecules form. “Our goal is to explore the relative importance of low-energy electrons versus photons in instigating the chemical reactions responsible for the extraterrestrial synthesis of these prebiotic molecules,” Barnes explains.
The few studies that previously probed this question suggested that both electrons and photons can catalyze the same reactions. Studies by Barnes and colleagues, however, hint that the prebiotic molecule yield from low-energy electrons and photons could be significantly different in space. “Our calculations suggest that the number of cosmic-ray-induced electrons within cosmic ice could be much greater than the number of photons striking the ice,” Barnes explains. “Therefore, electrons likely play a more significant role than photons in the extraterrestrial synthesis of prebiotic molecules.”

Earthly Implications of Space Research
Aside from cosmic ice, her research into low-energy electrons and radiation chemistry also has potential applications on Earth. Barnes and colleagues recently studied the radiolysis of water, finding evidence of electron-stimulated release of hydrogen peroxide and hydroperoxyl radicals, which destroy stratospheric ozone and act as damaging reactive oxygen species in cells.
“A lot of our water radiolysis research findings could be used in medical applications and medical simulations,” Barnes shares, offering the example of using high-energy radiation to treat cancer. “I once had a biochemistry professor say that humans are basically bags of water. So, other scientists are investigating how low-energy electrons produced in water affect our DNA molecules.”
She also says the team’s findings are applicable to environmental remediation efforts where wastewater is being treated with high-energy radiation, which produces large numbers of low-energy electrons that are assumed to be responsible for the destruction of hazardous chemicals.
Laboratory Simulations and Broader Impacts
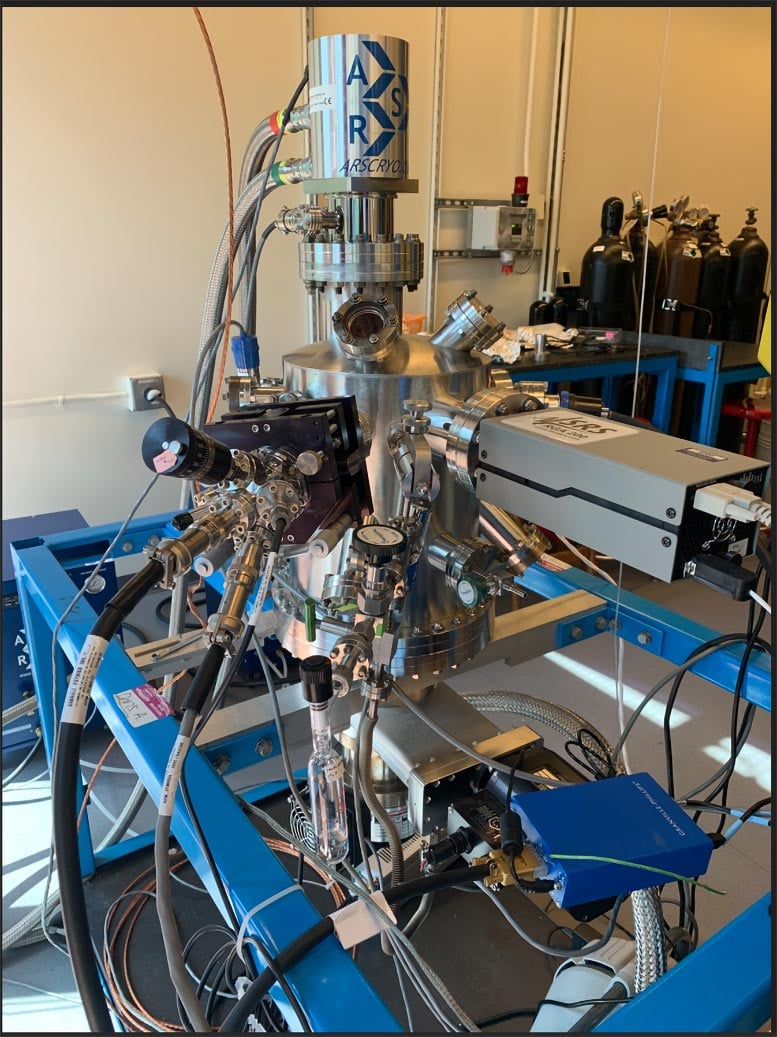
Back to space chemistry, in attempting to better understand prebiotic molecule synthesis, the researchers didn’t limit their efforts to mathematical modeling; they also tested their hypothesis by mimicking the conditions of space in the lab. They use an ultrahigh-vacuum chamber containing an ultrapure copper substrate that they can cool to ultralow temperatures, along with an electron gun that produces low-energy electrons and a laser-driven plasma lamp that produces low-energy photons. The scientists then bombard nanoscale ice films with electrons or photons to see what molecules are produced.
“Although we have previously focused on how this research is applicable to interstellar submicron ice particles, it is also relevant to cosmic ice on a much larger scale, like that of Jupiter’s moon Europa, which has a 20-mile-thick ice shell,” says Barnes.
Thus, she suggests their research will help astronomers understand data from space exploration missions such as NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope as well as the Europa Clipper, initially expected to launch in October 2024. Barnes hopes that their findings will inspire other researchers to incorporate low-energy electrons into their astrochemistry models that simulate what happens within cosmic ices.
Barnes and colleagues are also varying the molecular composition of ice films and exploring atom addition reactions to see if low-energy electrons can produce other prebiotic chemistries. This work is being performed in collaboration with researchers at the Laboratory for the Study of Radiation and Matter in Astrophysics and Atmospheres in France.
“There’s a lot that we’re on the cusp of learning, which I think is really exciting and interesting,” says Barnes, touting what she describes as a new Space Age.
The research was funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation, Arnold and Mabel Beckman Foundation, Wellesley College Faculty Awards, Brachman Hoffman grants, and the Nancy Harrison Kolodny ’64 Professorship.
Title
Extraterrestrial synthesis of prebiotic molecules
Abstract
We demonstrate for the first time that Galactic cosmic rays with energies as high as ∼ 1010 eV can trigger a cascade of low-energy (< 20 eV) secondary electrons that could be a significant contributor to the interstellar synthesis of prebiotic molecules whose delivery by comets, meteorites, and interplanetary dust particles may have kick-started life on Earth. For the energetic processing of interstellar ice mantles inside dark, dense molecular clouds, we explore the relative importance of low-energy (< 20 eV) secondary electrons—agents of radiation chemistry—and low-energy (< 10 eV), non-ionizing photons—instigators of photochemistry. Our calculations indicate fluxes of ∼ 102 electrons cm−2 s−1 for low-energy secondary electrons produced within inter-stellar ices due to incident attenuated Galactic cosmic-ray (CR) protons. Consequently, in certain star-forming regions where internal high-energy radiation sources produce ionization rates that are observed to be a thousand times greater than the typical interstellar Galactic ionization rate, the flux of low-energy secondary electrons should far exceed that of non-ionizing photons. Because reaction cross-sections can be several orders of magnitude larger for electrons than for photons, even in the absence of such enhancement, our calculations indicate that secondary low-energy (< 20 eV) electrons are at least as significant as low-energy (< 10 eV) non-ionizing photons in the interstellar synthesis of prebiotic molecules. Most importantly, our results demonstrate the pressing need to explicitly incorporate low-energy electrons in current and future astrochemical simulations of cosmic ices. In addition to these calculations, I will also discuss our most recent novel results pertaining to water radiolysis, which has been studied since 1901. Such calculations and experiments are critically important for interpreting James Webb Space Telescope infrared measurements, which are currently being used to probe the origins of life by studying molecules found in ices near star-forming regions.
Source link



