Ancient Predator Unearthed in Nevada Rewrites Triassic Coastal Life Story

A newly discovered Triassic crocodile relative demonstrates that pseudosuchian archosaurs inhabited global coastal areas, significantly enriching our understanding of Mesozoic marine ecosystems.
Researchers have discovered a new species of extinct crocodile relative from the Triassic Favret Formation of Nevada, USA. The species, named Benggwigwishingasuchus eremicarminis, reveals that the ancient crocodile kin known as pseudosuchian archosaurs dominated shorelines across the Middle Triassic globe between 247.2 and 237 million years ago. This finding, detailed in a study published on July 10 in Biology Letters, reshapes our understanding of coastal ecosystems during the early Age of Dinosaurs.
“This exciting new species demonstrates that pseudosuchians were occupying coastal habitats on a global basis during the Middle Triassic,” said Dr. Nate Smith, lead author of the paper, and Gretchen Augustyn Director and Curator of the Dinosaur Institute at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County.
Uncovering Pseudosuchian Diversity
The majority of fossils from the eastern Panthalassan Ocean of the Triassic, which includes the Favret Formation, are those of sea-going creatures such as ammonites or marine reptiles like the giant ichthyosaur C. youngorum. Therefore, the discovery of the newly described terrestrial species B. eremicarminis was quite unexpected.
“Our first reaction was: What the hell is this?” said co-author Dr. Nicole Klein of the University of Bonn. “We were expecting to find things like marine reptiles. We couldn’t understand how a terrestrial animal could end up so far out in the sea among the ichthyosaurs and ammonites. It wasn’t until seeing the nearly completely prepared specimen in person that I was convinced it really was a terrestrial animal.”
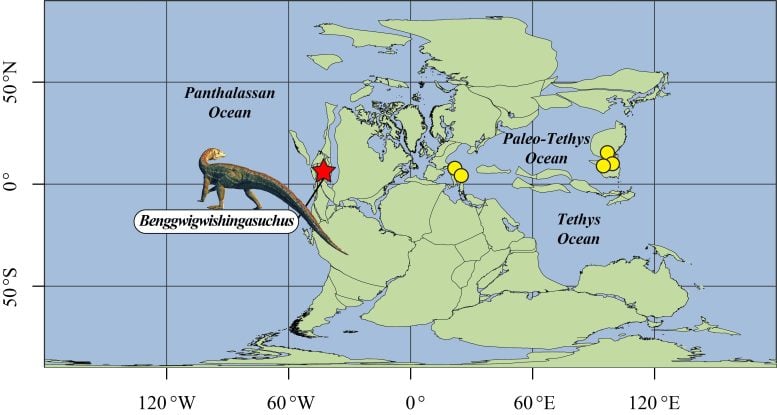
A map of the Middle Triassic oceans and the archosauriforms described from eastern coastal settings (yellow dots), as well as the new species B. eremicarminis from the Panthalassan coast (red star). Credit: Nate Smith
Evolutionary Insights from Fossil Discoveries
Pseudosuchian archosaurs have been unearthed in fossil beds from the shores of the ancient Tethys Ocean, but this is the first coastal representative from the Panthalassan Ocean and western hemisphere, revealing that these crocodile relatives were present in coastal environments worldwide during the Middle Triassic. Interestingly, these coastal species aren’t all from the same evolutionary group, suggesting that pseudosuchians (and archosauriforms more broadly) were independently adapting to life along the shores.
“Essentially, it looks like you had a bunch of very different archosauriform groups deciding to dip their toes in the water during the Middle Triassic. What’s interesting, is that it doesn’t look like many of these ‘independent experiments’ led to broader radiations of semi-aquatic groups,” said Smith.
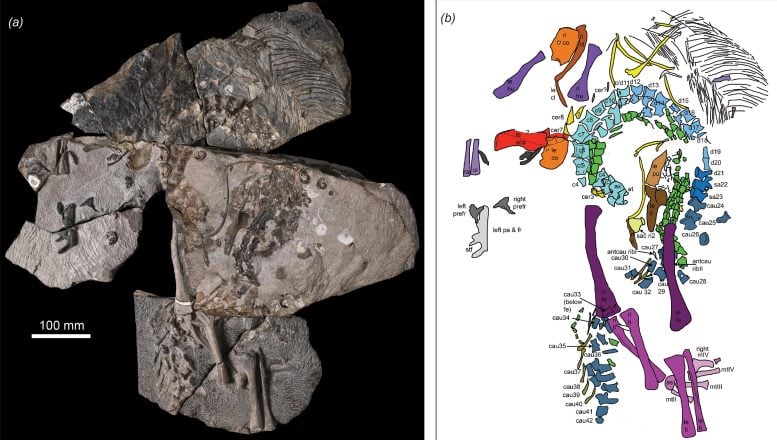
B. eremicarminis specimen a) overview of skeleton; b) color-coded interpretation of skeleton. Credit: photograph by Stephanie Abramowicz; drawing by Dr. Nicole Klein
Revealing Ancient Adaptations and Diverse Forms
During the Triassic, archosaurs, “the ruling reptiles,” arose and split into two groups with two surviving representatives: birds, the descendants of dinosaurs, and crocodilians (alligators, crocodiles, and gharials), the descendants of pseudosuchian archosaurs like B. eremicarminis. While today’s crocodilians are similar enough to be mistaken for one another by most people, their ancient relatives varied wildly in size and lifestyle. The evolutionary relationships of B. eremicarminis and its relatives suggest that pseudosuchians achieved great diversity very quickly following the End-Permian mass extinction—the extent of which is waiting to be discovered in the fossil record.
“A growing number of recent discoveries of Middle Triassic pseudosuchians are hinting that an underappreciated amount of morphological and ecological diversity and experimentation was happening early in the group’s history. While a lot of the public’s fascination with the Triassic focuses on the origin of dinosaurs, it’s really the pseudosuchians that were doing interesting things at the beginning of the Mesozoic,” Smith said.
Exploring the Ecology of B. eremicarminis
The new species underlines the multiplicity of these ancient reptiles during the Triassic, from giants like Mambawakale ruhuhu to smaller animals like the newly described B. eremicarminis, which probably reached around 5–6 feet in length. Exactly how long B. eremicarminis was and how it survived along the coasts remains shrouded in the past. Only a few elements of the individual’s skull were found, and any clues to how it fed and hunted are similarly absent. What’s more clear is that B. eremicarminis likely stuck pretty close to the shore. Its well-preserved limbs are well-developed without any of the signs of aquatic living like flippers or altered bone density.
The research team wanted a name that paid respect to the original human inhabitants of the Augusta Mountains where the specimen was found, and so consulted a member of the Fallon Paiute Shoshone Tribe to decide on an appropriate name.“Benggwi-Gwishinga”, a word that means “catching fish” in Shoshone, was combined with the Greek word for Sobek, the Egyptian crocodile-headed god, to coin the new genus, Benggwigwishingasuchus. The specific epithet eremicarminis translates to “desert song”, honoring two supporters of NHMLAC who have a passion for the paleontology and opera of the Southwest. Thus, the full name is meant to translate roughly as “Fisherman Croc’s Desert Song.”
Reference: “A new pseudosuchian from the Favret Formation of Nevada reveals that archosauriforms occupied coastal regions globally during the Middle Triassic” by Nathan D. Smith, Nicole Klein, P. Martin Sander and Lars Schmitz, 10 July 2024, Biology Letters.
DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2024.0136




