Unveiling the Hidden Satellites of the Milky Way

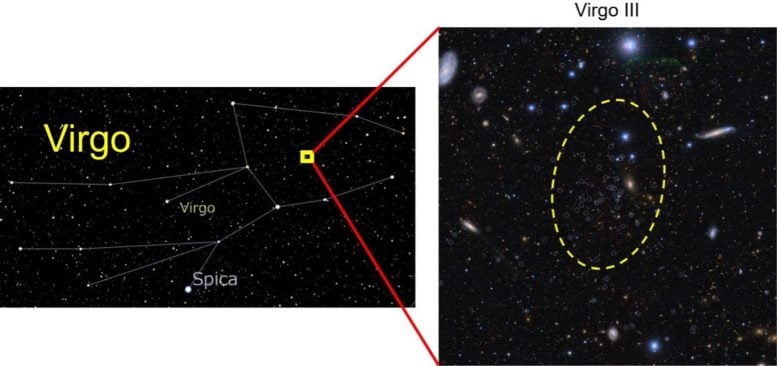
The position of a newly found dwarf galaxy (Virgo III) in the constellation Virgo (left) and its member stars (right; those circled in white). The member stars are concentrated inside the dashed line in the right panel. Credit: NAOJ/Tohoku University
Researchers discovered two new satellite galaxies of the Milky Way using the Subaru telescope, hinting at a higher number of satellites than previously thought and indicating a shift from a deficit to a surplus in expected galaxy counts.
For years, astronomers have worried about how to explain why the Milky Way has fewer satellite galaxies than the standard dark matter model predicts. This is called the “missing satellites problem.” In order to bring us closer to solving this problem, an international team of researchers used data from the Hyper Suprime-Cam (HSC) Subaru Strategic Program (SSP) to discover two completely new satellite galaxies.
These results were recently published in the Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan by a team of researchers from Japan, Taiwan, and America.
The Role of Satellite Galaxies in Understanding Dark Matter
We live in a galaxy called The Milky Way, which has other, smaller galaxies orbiting it called satellite galaxies. Studying these satellite galaxies can help researchers unravel mysteries surrounding dark matter, and better understand how galaxies evolve over time.
“How many satellite galaxies does the Milky Way have? This has been an important question for astronomers for decades,” remarks Masahi Chiba, a professor at Tohoku University.
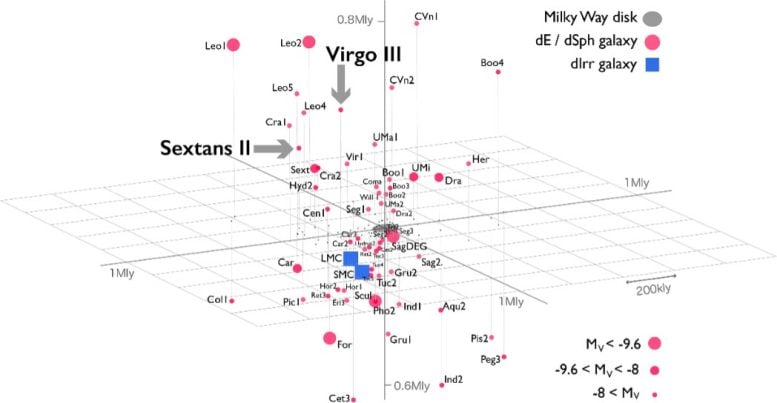
Satellite galaxies around the Milky Way Galaxy. The plane of the Galactic disk is on the horizontal plane. The blue squares are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, and the red circles are other satellite galaxies. The fainter their absolute visual magnitude, the smaller the dot size. Credit: NAOJ/Tohoku University
Discoveries of Dwarf Galaxies With the Subaru Telescope
The research team recognized the possibility that there are likely many undiscovered, small satellite galaxies (dwarf galaxies) that are far away and difficult to detect. The powerful ability of the Subaru telescope — which sits atop an isolated mountain above the clouds in Hawaii — is well-suited to find these galaxies. In fact, this research team previously found three new dwarf galaxies using the Subaru telescope.
Now, the team has discovered an additional two new dwarf galaxies (Virgo III and Sextans II). With this discovery, a total of nine satellite galaxies have been found overall by different research teams. This is still much fewer than the 220 satellite galaxies predicted by the standard theory of dark matter.
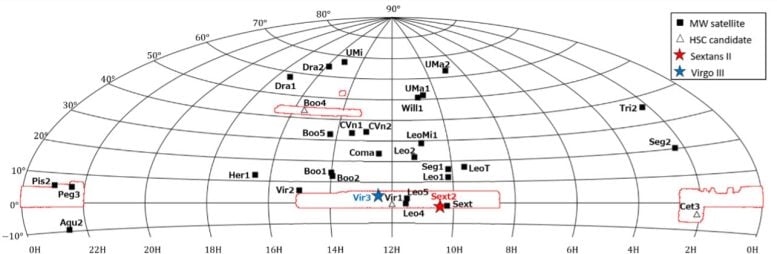
The area observed by the HSC-SSP (area surrounded by red lines). Previously known satellite galaxies are indicated by black squares, and newly discovered satellite galaxies are indicated by white triangles and stars. Credit: NAOJ/Tohoku University
The Changing Perspective on Satellite Galaxy Numbers
However, the footprint of the HSC-SSP does not cover the entire Milky Way. If the distribution of those nine satellite galaxies across the entire Mily Way is similar to what was found in the footprint captured by the HSC-SSP, the research team calculates that there actually may be closer to 500 satellite galaxies. Now, we are faced with a “too many satellites problem,” rather than a “missing satellites problem.”
To better characterize the actual amount of satellite galaxies, more high-resolution imaging and analysis is required. “The next step is to use a more powerful telescope that captures a wider view of the sky,” explains Chiba, “Next year, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile will be used to fulfill that purpose. I hope that many new satellite galaxies will be discovered.”
Reference: “Final results of the search for new Milky Way satellites in the Hyper Suprime-Cam Subaru Strategic Program survey: Discovery of two more candidates” by Daisuke Homma, Masashi Chiba, Yutaka Komiyama, Masayuki Tanaka, Sakurako Okamoto, Mikito Tanaka, Miho N Ishigaki, Kohei Hayashi, Nobuo Arimoto, Robert H Lupton, Michael A Strauss, Satoshi Miyazaki, Shiang-Yu Wang and Hitoshi Murayama, 8 June 2024, Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan.
DOI: 10.1093/pasj/psae044



